Introduction
The poultry industry has seen exponential growth over the last few decades, driven by the demand for high-quality protein sources such as chicken. However, the intensification of poultry production has also brought challenges, particularly in managing the health of broilers, which are reared under conditions that can predispose them to stress and diseases. Among these, gut health is a critical area of focus because it directly influences the overall health, performance, and productivity of the birds.

Traditionally, antibiotics have been used extensively to manage gut health issues and prevent diseases. However, the rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and global consumer demand for antibiotic-free poultry has necessitated a shift toward non-antibiotic solutions. Phytomolecules, bioactive compounds derived from plants, have emerged as a promising alternative for maintaining gut health in broilers. This article delves into the significance of gut health in broilers, explores the role of phytomolecules and highlights their effectiveness as a sustainable solution in modern poultry operations.
Understanding Gut Health in Broilers
Gut health refers to the optimal functioning of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which is essential for nutrient absorption, immune response, and overall well-being of broilers. In poultry, the gut is not only responsible for digestion but also acts as a key barrier against pathogens, playing a critical role in the immune system. (Image 1)
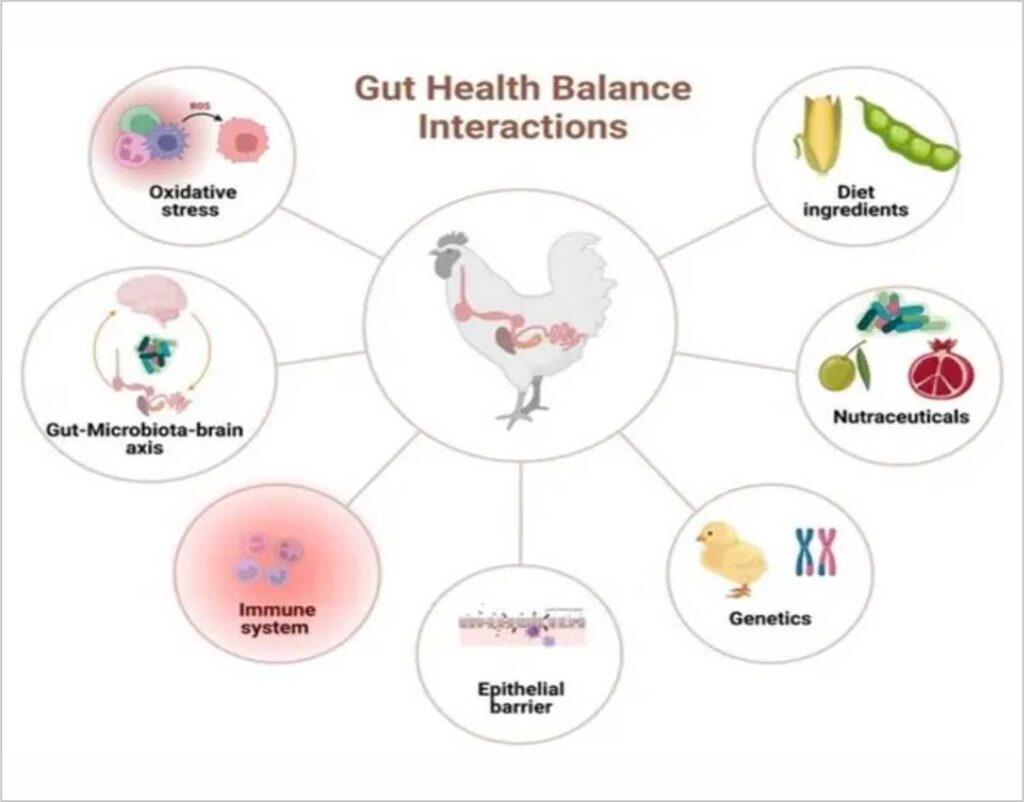
(Image 1) Source: Guillermo Tellez-Isaias et al 2023, Engormix
A healthy gut consists of a balanced microbial population (microbiota), an intact intestinal barrier, and a well-regulated immune response. Any imbalance in these components can lead to gut dysfunction, manifesting as poor nutrient absorption, diarrhoea, increased susceptibility to infections, and reduced growth performance.
Common gut health challenges in broilers include:
1. Dysbiosis: An imbalance in the gut microbiota, often caused by stress, poor nutrition, or infections, can disrupt gut function.
2. Enteric diseases: Diseases like necrotic enteritis (caused by Clostridium perfringens) and coccidiosis (caused by Eimeria species) can severely damage the intestinal lining.
3. Leaky gut syndrome: Increased intestinal permeability can allow harmful substances to pass into the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and immune responses.
4. Poor nutrient absorption: Impaired gut function can reduce the efficiency of nutrient absorption, affecting growth rates and feed conversion ratios.

Source: Self Field observations
Maintaining optimal gut health is, therefore, essential to achieving high productivity, reducing mortality, and ensuring efficient feed utilization in broilers.
The Role of Phytomolecules in Gut Health
Phytomolecules are bioactive compounds derived from plants, including essential oils, alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, and terpenes. These molecules possess a wide range of biological activities, such as antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties, making them effective in maintaining and improving gut health.
Over the years, research has demonstrated the potential of phytomolecules to support gut health in poultry. Several studies have shown that these plant-derived compounds can modulate the gut microbiota, strengthen the intestinal barrier, and enhance immune responses, thus promoting better growth and health in broilers.
1. Antimicrobial Properties
One of the primary benefits of phytomolecules is their ability to exert antimicrobial effects. Many essential oils and plant extracts contain compounds like carvacrol, thymol, and eugenol, which have been found to inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Clostridium perfringens. These antimicrobial properties help maintain a balanced gut microbiota, reducing the risk of infections and dysbiosis. (Image 2)
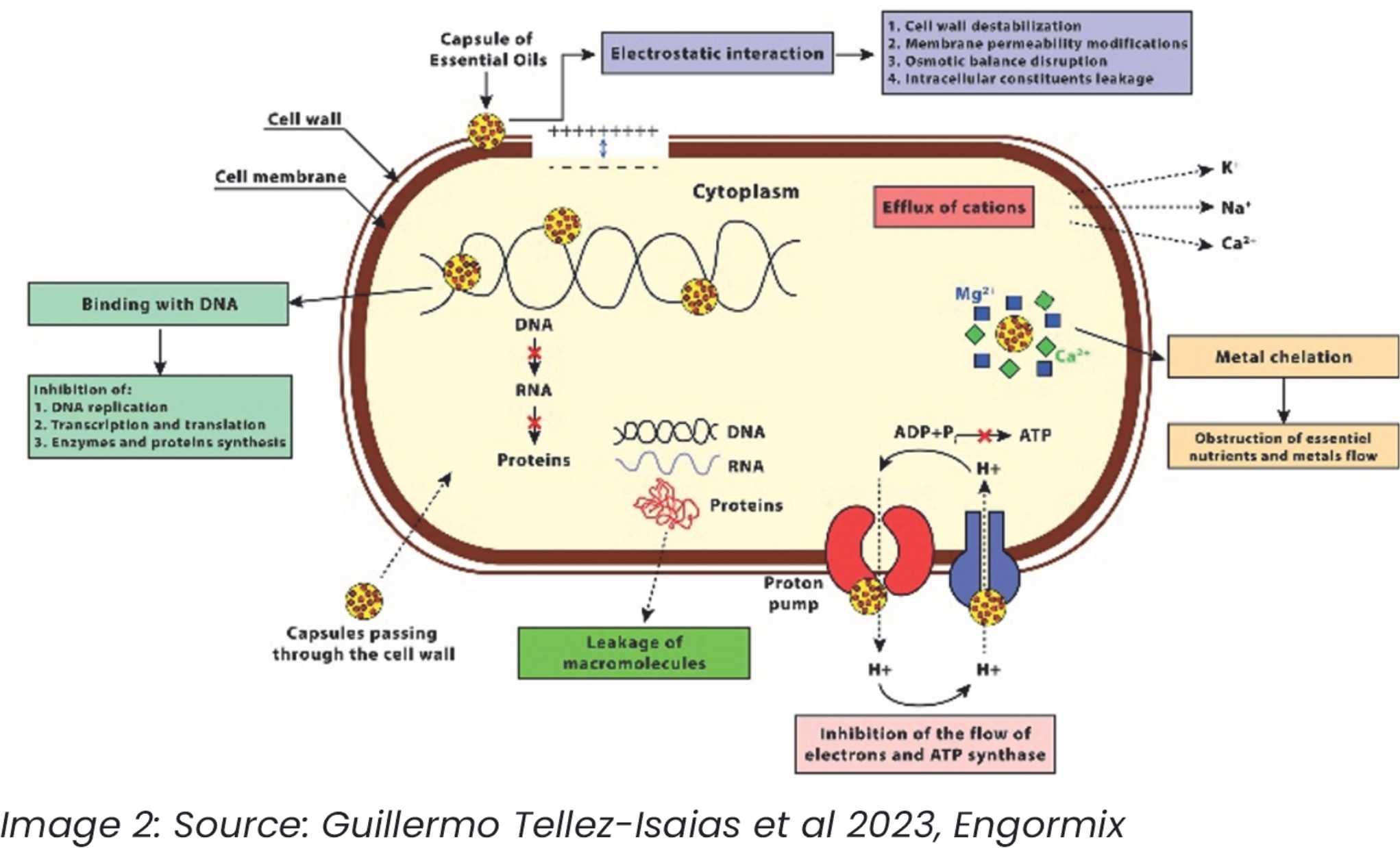
A study by Burt (2004) demonstrated that essential oils containing carvacrol and thymol are effective in inhibiting the growth of Salmonella and Campylobacter in broilers. Similarly, Liu et al. (2012) found that phytogenic compounds such as oregano and thyme oils can significantly reduce the colonization of pathogenic bacteria in the poultry gut.
2. Antioxidant Effects
Oxidative stress is a common challenge in modern poultry production, especially under intensive farming conditions. Excessive oxidative stress can damage the intestinal lining, leading to inflammation and compromised gut integrity. Phytomolecules such as flavonoids and phenolic acids have strong antioxidant properties, which help neutralize free radicals and protect the intestinal cells from oxidative damage. (Image 3)
Flavonoids, such as quercetin and catechins, have been shown to enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes, reduce inflammation, and promote gut integrity. In a study conducted by Rehman et al. (2020), supplementation with flavonoid-rich plant extracts improved the gut health of broilers by reducing oxidative stress and enhancing the intestinal barrier function.
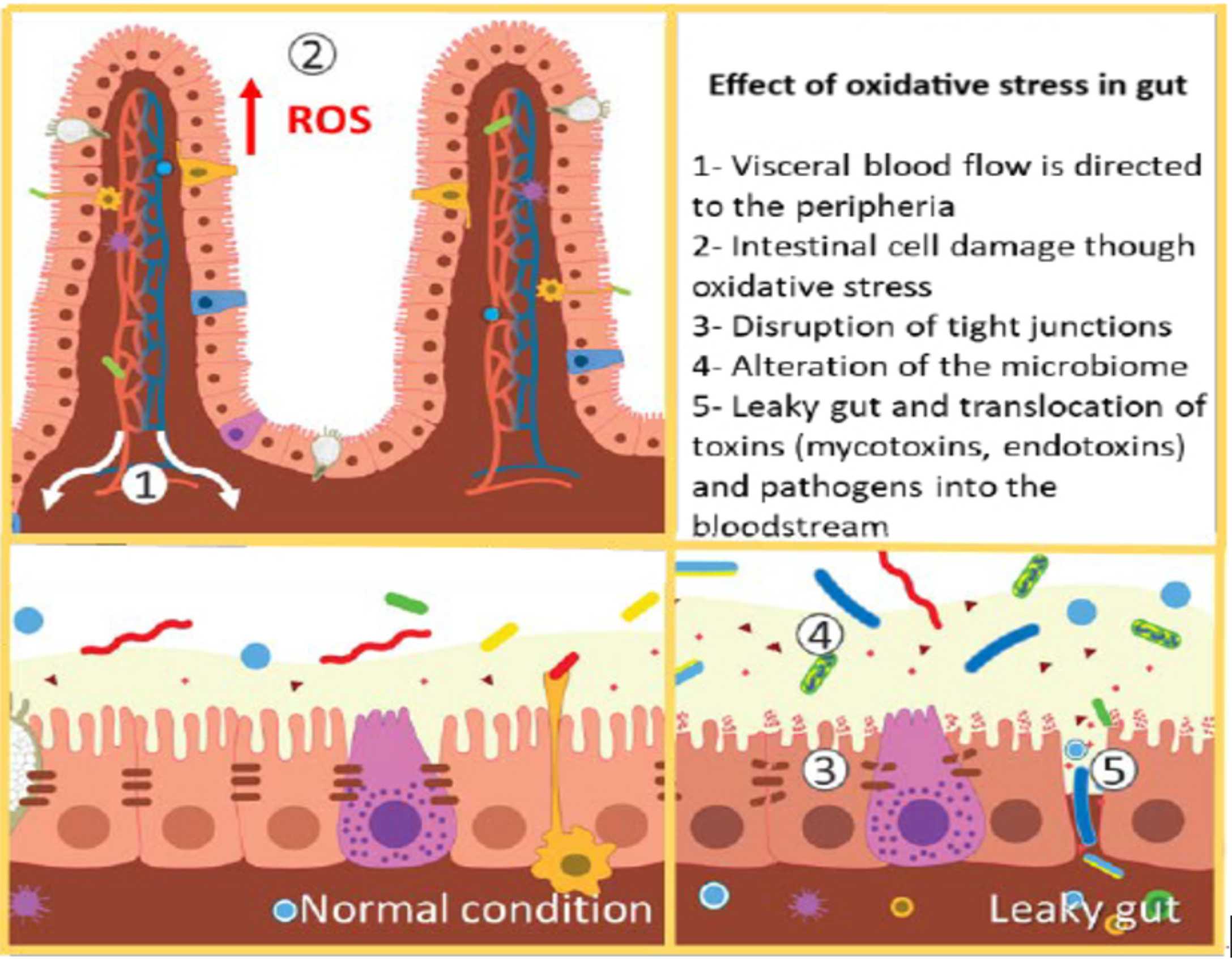
(Image 3) Source: Yammine, Jina et al. Heliyon, Volume 8, Issue 12, e12472
3. Anti-inflammatory Action
Chronic inflammation in the gut can lead to poor nutrient absorption, tissue damage, and increased susceptibility to infections. Phytomolecules possess anti-inflammatory properties that can mitigate gut inflammation and support tissue repair. Compounds such as curcumin (found in turmeric) and gingerols (found in ginger) are well-known for their anti-inflammatory effects. A study by Khaleel et al. (2021) demonstrated that dietary supplementation with curcumin significantly reduced gut inflammation in broilers and improved their overall performance. Similarly, ginger extract has been found to decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhance gut health in poultry.
4. Enhancing the Intestinal Barrier
The intestinal barrier is the first line of defence against harmful pathogens and toxins. Phytomolecules, particularly tannins and essential oils, can strengthen the intestinal lining by promoting the production of tight junction proteins that seal the spaces between intestinal cells. This helps reduce intestinal permeability (leaky gut) and prevents the translocation of harmful substances into the bloodstream. (Image 4)
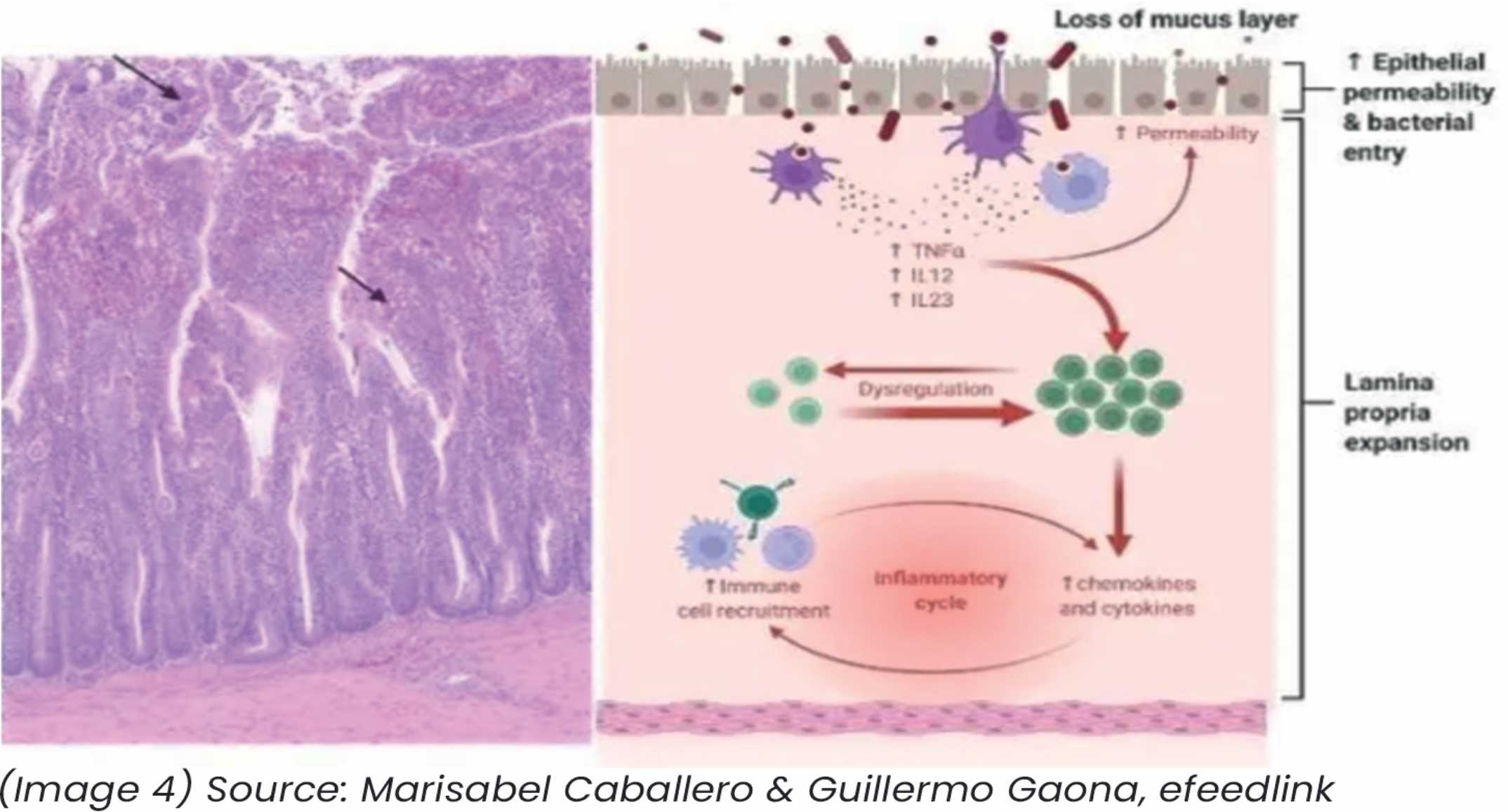
In a study by Yang et al. (2015), tannin-rich plant extracts were found to enhance the expression of tight junction proteins in the intestinal mucosa of broilers, resulting in improved gut integrity and reduced incidence of leaky gut.
5. Modulating the Gut Microbiota
Phytomolecules have prebiotic effects that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while inhibiting pathogenic bacteria. A balanced gut microbiota plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health by enhancing nutrient absorption, stimulating the immune system, and protecting against infections.
Research by Windisch et al. (2008) found that phytogenic feed additives, including essential oils and polyphenols, can modulate the gut microbiota by promoting beneficial bacteria and reducing pathogenic bacterial populations. This microbiota modulation helps maintain gut homeostasis, which is essential for optimal growth and performance in broilers.
Phytomolecules in Commercial Broiler Production
The use of phytomolecules as feed additives in broiler production is gaining popularity as a natural and effective alternative to antibiotics. Various commercial phytogenic products containing essential oils, plant extracts, and other bioactive compounds are now available for use in poultry diets.
Benefits of Phytomolecules Supplementation
1. Improved Growth Performance: Several studies have shown that phytomolecules supplementation can enhance growth rates, feed conversion ratios, and overall performance in broilers. For example, Yang et al. (2015) reported that broilers supplemented with a blend of essential oils and polyphenols exhibited higher weight gain and better feed efficiency.
2. Reduced Mortality and Morbidity: By promoting gut health and enhancing the immune system, phytomolecules help reduce the incidence of enteric diseases and lower mortality rates in broilers. A study by Ciftci et al. (2010) found that broilers fed with a diet containing thyme and rosemary essential oils had a lower incidence of necrotic enteritis and improved survival rates.
3. Enhanced Feed Efficiency: Phytomolecules improve nutrient absorption by maintaining gut integrity and supporting the activity of digestive enzymes. This leads to better feed efficiency and reduced feed costs, which are critical factors in commercial broiler production.
4. Sustainability and Consumer Acceptance: The use of phytogenic feed additives aligns with the growing consumer demand for antibiotic-free poultry products. As these additives are derived from natural sources, they are perceived as safe and environmentally friendly, contributing to the sustainability of poultry production.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of phytomolecules in poultry production are well-documented, there are some challenges associated with their use.
These include:
– Variability in Efficacy: The efficacy of phytomolecules can vary depending on factors such as plant source, extraction method, dosage, and the overall diet composition. Standardization of phytogenic products is essential to ensure consistent results.
– Cost: Phytogenic feed additives can be more expensive than traditional antibiotics. However, the long-term benefits, including improved bird health and performance, can offset the higher initial costs.
– Regulatory Approval: Globally in some regions, the use of certain phytomolecules in animal feed may be subject to regulatory approval. Producers should ensure that the phytogenic products they use comply with local regulations.
Conclusion
Gut health is a cornerstone of successful broiler production, influencing not only the health and welfare of the birds but also their growth performance and profitability. As the poultry industry continues to shift toward antibiotic-free production systems, phytomolecules offer a natural and effective solution for maintaining gut health in broilers.
By leveraging the antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and microbiota-modulating properties of phytomolecules, poultry producers can improve gut integrity, reduce the incidence of enteric diseases, and enhance the overall performance of their birds. The multiple mechanisms through which phytomolecules support gut health, such as promoting beneficial microbial populations, protecting the intestinal barrier, and mitigating oxidative stress, make them a valuable tool in the pursuit of sustainable poultry production.
The growing body of research supporting the efficacy of phytomolecules in improving broiler gut health underscores their potential as a reliable alternative to antibiotics. Studies have consistently demonstrated that these plant-derived compounds can improve growth performance, reduce mortality, and enhance feed efficiency, all while aligning with consumer demands for natural, antibiotic-free products.
In conclusion, phytomolecules represent a promising, natural solution for enhancing gut health in broilers, offering benefits that extend beyond disease prevention to improving overall flock performance. As the poultry industry moves toward more sustainable and consumer-friendly practices, phytomolecules will likely play an increasingly important role in maintaining the health and productivity of broilers in antibiotic-free production systems.
The future of broiler production lies in sustainable practices that prioritize animal health and welfare without relying on antibiotics. Phytomolecules offer a natural and scientifically backed solution to the challenges of maintaining gut health in broilers, making them a critical component of the next generation of poultry feed additives.
References:
References are available on request.






